Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) presents a non-invasive therapeutic approach for a range of conditions, including depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). This innovative treatment employs magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells within the brain, aiming to alleviate symptoms. Remarkably, TMS has demonstrated effectiveness surpassing that of conventional medications and can also be utilized alongside pharmaceuticals.
What Does a TMS Treatment Session Look Like?
During a TMS session, an electromagnetic coil is gently applied to the scalp near the forehead, securely adhering to the skin. This coil administers magnetic pulses to specific brain regions responsible for mood regulation. TMS functions by activating crucial brain areas that may trigger or exacerbate various mental health disorders, including certain types of headaches like migraines. Various TMS treatment protocols are available, all requiring only a few minutes per session, and a series of such treatments can yield lasting results extending over several months.
For individuals seeking depression treatment, TMS often becomes a viable option when conventional medication approaches have proven ineffective. It’s important to note that trying TMS doesn’t necessitate exhausting all other options beforehand. Furthermore, TMS therapy is commonly covered by major insurance plans. In cases of depression, TMS can be instrumental in influencing the brain areas responsible for depressive symptoms.
TMS Therapy: Anxiety and Depression Medications

Traditional depression therapy primarily involves medication and mental health services. TMS can serve as a valuable complement to or even a replacement for these approaches. However, it’s crucial to consult with your prescribing physician before making any changes to your existing medications. While TMS can be used in conjunction with other forms of therapy, it’s unsafe to make medication adjustments independently.
In the realm of anxiety treatment, typical approaches often encompass medication and mental health services. Given the frequent co-occurrence of depression and anxiety, they are frequently addressed simultaneously, as they can reinforce each other. Anxiety typically manifests as excessive worry and frustration, which can exacerbate depression. Additionally, anxiety can lead to sleep disturbances such as insomnia, a condition that TMS therapy can also address.
Success with OCD and PTSD
TMS therapy has shown promise in assisting individuals with OCD and PTSD, two prevalent mental health disorders.
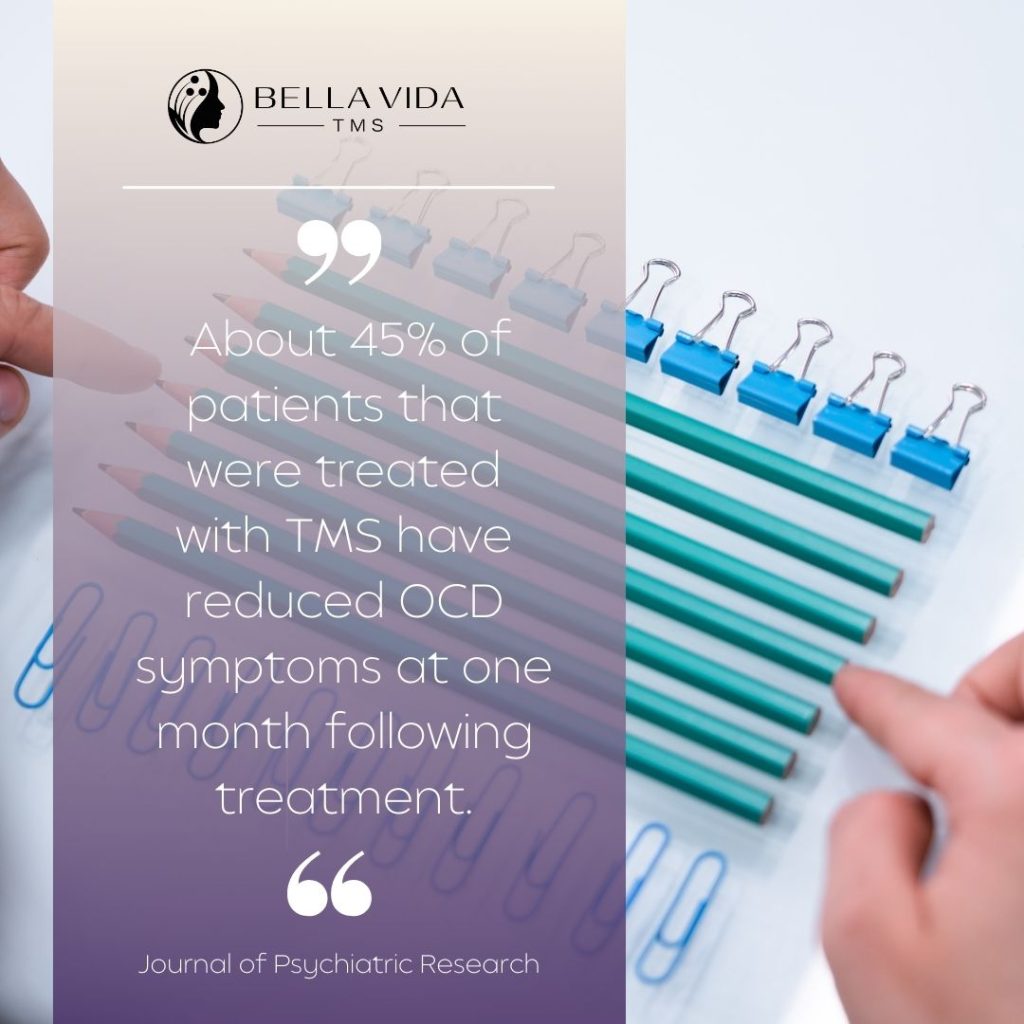
Research indicates that 45 percent of OCD patients experience a reduction in symptoms just one month after undergoing TMS.
A literature review of 20 studies suggests that TMS is an effective treatment for PTSD, with results lasting for months.
During TMS sessions, healthcare providers can pinpoint specific brain regions associated with various mental health conditions.
This process essentially “rewires” the brain, instructing it to reduce or even eliminate symptoms.
TMS Therapy: The Holistic Approach to Mental Health Treatment
TMS therapy offers a holistic approach to mental health. It is safe, effective, non-invasive, and requires no downtime. Various TMS protocols exist, with the most widely covered by insurance requiring just a few minutes per day for no more than two weeks to achieve optimal results. TMS is suitable for both adolescents and adults and can be used in conjunction with other therapeutic methods.
Accelerated forms of TMS therapy are available for individuals seeking expedited treatment or those traveling from out of state or abroad. These accelerated treatments are not typically covered by insurance but provide an efficient option for those in need. TMS has demonstrated its potential to address conditions such as depression, anxiety, PTSD, and OCD. If you’re exploring alternative options for other concerns, consider reaching out to determine if TMS could be a suitable solution. TMS therapy boasts few contraindications, making it an accessible option for most individuals.
External Reference links
- National Institutes of Health – Efficacy and clinical predictors of response to rTMS treatment in pharmacoresistant obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
- Journal of Psychiatric Research – Real-world efficacy of deep TMS for obsessive-compulsive disorder: Post-marketing data collected from twenty-two clinical sites
- Psychiatry Research – Real world efficacy and safety of various accelerated deep TMS protocols for major depression




